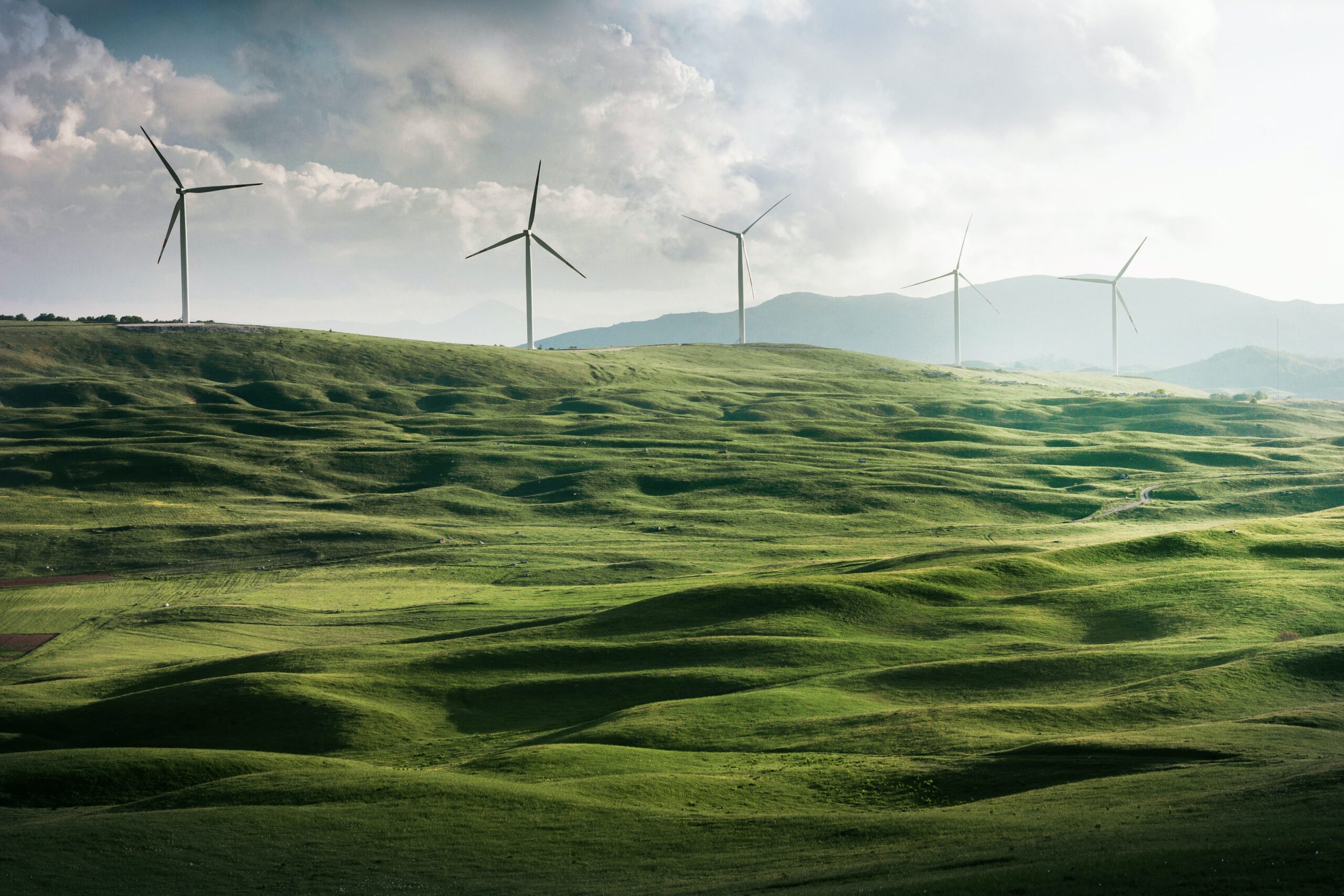
The project focuses on off-grid electrolyser plant optimisation. CLIC coordinated the development of the project consortium as well as the Business Finland co-innovation funding application, and the project is led by LUT. The proposal was submitted in April 2023. The total budget of the project is 3.7 M€, and Business Finland is funding 2.1 M€.
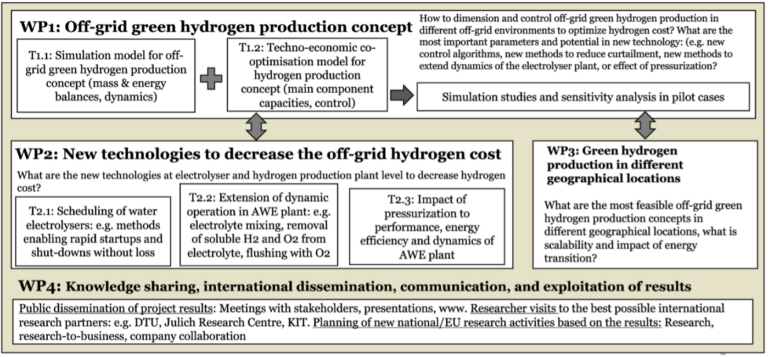 Figure 1: Work packages in Offgrid H2
Figure 1: Work packages in Offgrid H2
OffgridH2
OffgridH2 aims to understand the system parameters needed to reach the minimum cost of baseload hydrogen (LCOH) in off-grid hydrogen production environments. Furthermore, the project will explore technological solutions in water electrolysis plants and hydrogen storage to reduce LCOH. Additionally, the project will study pilot cases to identify the most feasible geographical locations to produce off-grid green hydrogen.
 Figure 2: OffgridH2 project consortium members
Figure 2: OffgridH2 project consortium members
The Consortium
The consortium consists of a public research project led by LUT University and private R&D projects led by Sumitomo SHI FW, Flexens, 3Flash, and VaasaETT. In addition, UPM Energy, Elcogen, Convion, and Suomen Hyötytuuli are financially supporting the public research project. The project has in-kind support from two leading ecosystems funded by Business Finland: Green Electrification 2035, led by ABB, and Zero Emission Marine, led by Wärtsilä.
Objectives
This co-innovation project aims to introduce new technologies and ideas that will improve the hydrogen yield of electrolyser plants and the overall efficiency of electrolysers attached to off-grid renewable electricity production units. By optimising the off-grid electrolysers, the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of hydrogen production can be increased. This lowers the cost of green hydrogen and increases its production volume, offering better competitiveness for energy and chemical industries using and refining the hydrogen. By improving the availability of low-cost green hydrogen, attractive new business opportunities and significant market potential can be created in the whole hydrogen value chain for Finnish companies.
By making the electrolysers more efficient and capable of utilising variable load conditions, quicker and more feasible implementation of large-scale green hydrogen production can be achieved. Hence, the optimisation of off-grid electrolyser plants will improve the economic viability of green hydrogen compared to fossil-based alternatives, help preserve raw materials, and greatly reduce the environmental impacts of industries and transportation.
If you have any questions regarding the project, kindly contact:
Jero Ahola, LUT University, jero.ahola@lut.fi